描述
海上有许多灯塔,为过路船只照明。

(图一)
如图一所示,每个灯塔都配有一盏探照灯,照亮其东北、西南两个对顶的直角区域。探照灯的功率之大,足以覆盖任何距离。灯塔本身是如此之小,可以假定它们不会彼此遮挡。
(图二)
若灯塔A、B均在对方的照亮范围内,则称它们能够照亮彼此。比如在图二的实例中,蓝、红灯塔可照亮彼此,蓝、绿灯塔则不是,红、绿灯塔也不是。
现在,对于任何一组给定的灯塔,请计算出其中有多少对灯塔能够照亮彼此。
输入
共n+1行。
第1行为1个整数n,表示灯塔的总数。
第2到n+1行每行包含2个整数x, y,分别表示各灯塔的横、纵坐标。
输出
1个整数,表示可照亮彼此的灯塔对的数量。
样例
输入
3
2 2
4 3
5 1
输出
1
限制
对于90%的测例:
对于95%的测例:
全部测例:
灯塔的坐标x, y是整数,且不同灯塔的x, y坐标均互异

时间:2 sec
内存:256 MB
提示
注意机器中整型变量的范围,C/C++中的int类型通常被编译成32位整数,其范围为![[-2^{31},2^{31}-1]](http://fenxiangle.me/wp-content/themes/hmj-blog/images/loading.gif) ,不一定足够容纳本题的输出。
,不一定足够容纳本题的输出。
算法思路
根据题意,对于灯塔对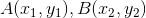
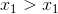
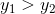
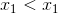
 即可
即可
解法一:暴力解法
struct Point
{
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
};
Point* points = new Point[4000001];
bool isGroup(Point& a, Point& b)
{
return (a.x > b.x && a.y > b.y || a.x < b.x && a.y < b.y);
}
int main()
{
int n = 0;
scanf("%d\n", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
scanf("%d\n", &points[i].x);
scanf("%d\n", &points[i].y);
}
int rel = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j)
{
if (isGroup(points[i], points[j]))
rel++;
}
}
printf("%d\n", rel);
}解法二:
先将各个灯塔根据x坐标排序,然后取出y坐标,对y坐标进行归并排序的同时,计数“顺序对”,将B数组(下标为j,lo~mi)与C数组(下标为k,mi~hi)归并时,当B[j] < C[k],B[j]也必小于C[k + mi]~C[hi],构成(hi - mi - k)个顺序对
#include <cstdio>
struct Point
{
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
};
bool isGroup(Point& a, Point& b);
void merge(Point* points, int lo, int mi, int hi);
void mergeSort(Point* points, int lo, int hi);
long long invInside(int* pointYs, int lo, int hi);
long long invBetween(int* pointYs, int lo, int mi, int hi);
Point* points = new Point[4000001];
Point* B = new Point[4000001];
int* pointYs = new int[4000001];
int* BY = new int[4000001];
int main()
{
#ifndef _OJ_
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
//setvbuf(stdin, new char[1 << 20], _IOFBF, 1 << 20);
int n = 0;
scanf("%d\n", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
scanf("%d\n", &points[i].x);
scanf("%d\n", &points[i].y);
}
mergeSort(points, 0, n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
pointYs[i] = points[i].y;
long long rel = invInside(pointYs, 0, n);
printf("%lld\n", rel);
#ifndef _OJ_
fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);
#endif
return 0;
}
bool isGroup(Point& a, Point& b)
{
return (a.x > b.x && a.y > b.y || a.x < b.x && a.y < b.y);
}
void merge(Point* points, int lo, int mi, int hi)
{
Point* A = points + lo;
int lb = mi - lo; // Point* B = new Point[lb];
for (size_t i = 0; i < lb; B[i] = A[i++]);
int lc = hi - mi; Point* C = points + mi;
for (int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0; j < lb; )
{
if (lc <= k || B[j].x < C[k].x) A[i++] = B[j++];
if (k < lc && C[k].x <= B[j].x) A[i++] = C[k++];
}
//delete[] B;
}
void mergeSort(Point* points, int lo, int hi)
{
if(hi - lo < 2) return;
int mi = (hi + lo) >> 1;
mergeSort(points, lo, mi);
mergeSort(points, mi, hi);
merge(points, lo, mi, hi);
}
long long invInside(int* pointYs, int lo, int hi)
{
long long rel = 0;
if (hi - lo < 2) return 0;
const int mi = (lo + hi) >> 1;
rel += invInside(pointYs, lo, mi);
rel += invInside(pointYs, mi, hi);
rel += invBetween(pointYs, lo, mi, hi);
return rel;
}
long long invBetween(int* pointYs, int lo, int mi, int hi)
{
int* A = pointYs + lo;
int lb = mi - lo; // int* B = new int[lb];
for (size_t i = 0; i < lb; BY[i] = A[i++]);
int lc = hi - mi; int* C = pointYs + mi;
long long num = 0;
for (size_t i= 0, j = 0, k = 0; j < lb;)
{
if (lc <= k || (BY[j] <= C[k]))
{
A[i++] = BY[j++];
if (k < lc)
num += lc - k;
}
if ((k < lc) && C[k] <= BY[j])
A[i++] = C[k++];
}
//delete[] B;
return num;
}不预先定义归并排序Point数组B,与Y坐标数组归并排序的数组B,会超时
转载自原文链接, 如需删除请联系管理员。
原文链接:灯塔(LightHouse),转载请注明来源!
